Design Thinking: Problem Solving with a Difference
If you’re in the business of product development, you’ll know what it is to come across a knotty problem.
Design thinking can really help you here. It’s a step-by-step approach to practical problem solving, allowing you to concretize your ideas. We’ll set out everything you need to know below.
What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking was founded as a method in 1991, by Larry Leifer (a Stanford Professor), Terry Winograd, and David Kelley. Since 2007, Design Thinking, together with its implementation and further research, has been funded by the Hasso Plattner Institute.
The basic assumption of the three developers is that problems can be better solved when people from different disciplines work together in a creative and open environment, discussing issues and proposing solutions jointly, and always taking into account the needs and motivations of the target group. Curiosity and creative openness are prerequisites for this process.
Design thinking is a systematic approach to complex problems from all areas of life. In contrast to many other models of problem solving, the focus is on user needs and wants, as well as user-oriented invention.
What does Design Thinking aim to do?
The goal of the Design Thinking method is to creatively solve problems and develop new and innovative ideas. The method is primarily intended for interdisciplinary teams and is designed to facilitate the work of all participants. For this purpose, different experiences, opinions and perspectives on a problem are collected and brought together to develop a strategy for change and improvement.
Design Thinking is already successfully used by many international companies, such as Porsche, VW and Siemens. The method is intended to ensure the highest possible benefit for customers, which means that the customer’s wishes and needs are front and center.
Why is the Design Thinking model so successful?
The multidisciplinary team, the space and the process are treated as equally important elements in order to find new possibilities and unconventional approaches to solutions. Design Thinking’s success comes from this unique blend of working and thinking.
In this context, multidisciplinary team means a team of five or six people from different disciplines, assembled to work on problem solving. The diversity of thought, and the freedom to communicate with other teams, leads to a high success rate in achieving goals.
Thespace is designed on the basis that ideas unfold best in a free and flexible environment. This includes a large enough office, well equipped for finding solutions to problems (whiteboards, etc.).
The Design Thinking process runs in six interactive loops and is thus tested over and over again. (See the section “How does Design Thinking work? – The 6 phases”).
How Design Thinking optimizes the path to customer-centric solutions
Design Thinking requires constant feedback between the team, potential solutions and the target group. These three elements remain constantly connected. Processes and behaviors are analyzed in detail.
Initial solution approaches and ideas are ideated as early as possible in the form of prototypes, so that potential customers can test them – before completion or market launch – and provide feedback. In this way, design thinking generates practical and customer-centric results.
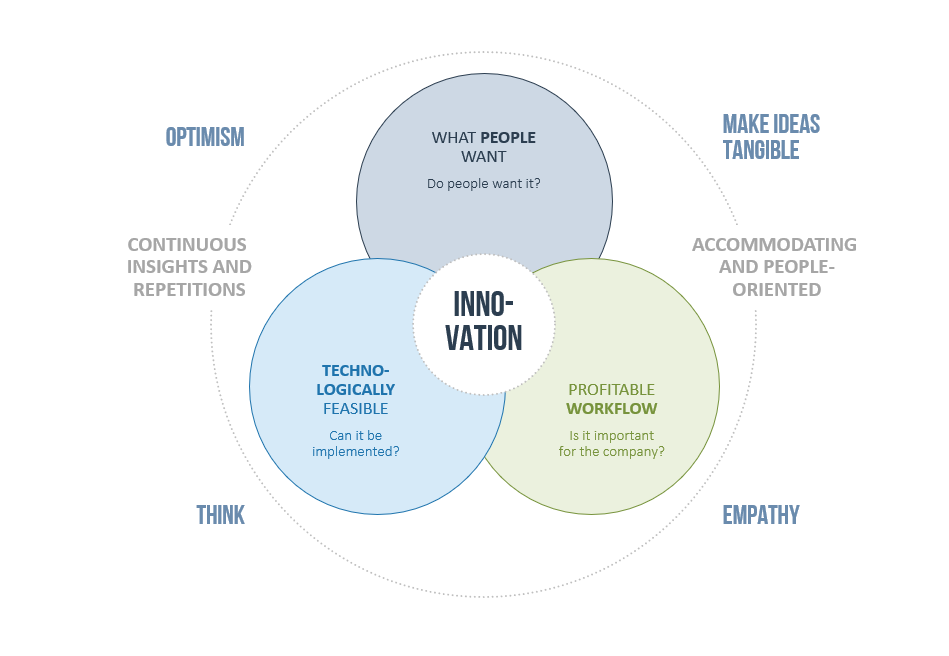
It its innovative approach to problem-solving, Design Thinking considers three essential components:
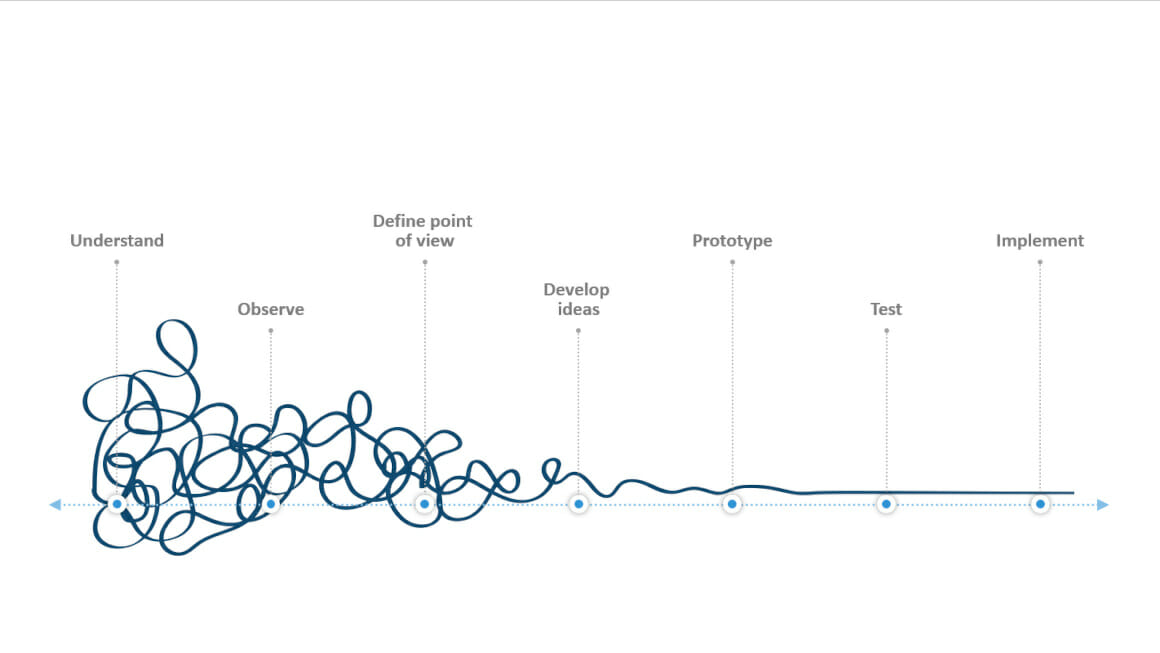
How does Design Thinking work? – The six phases
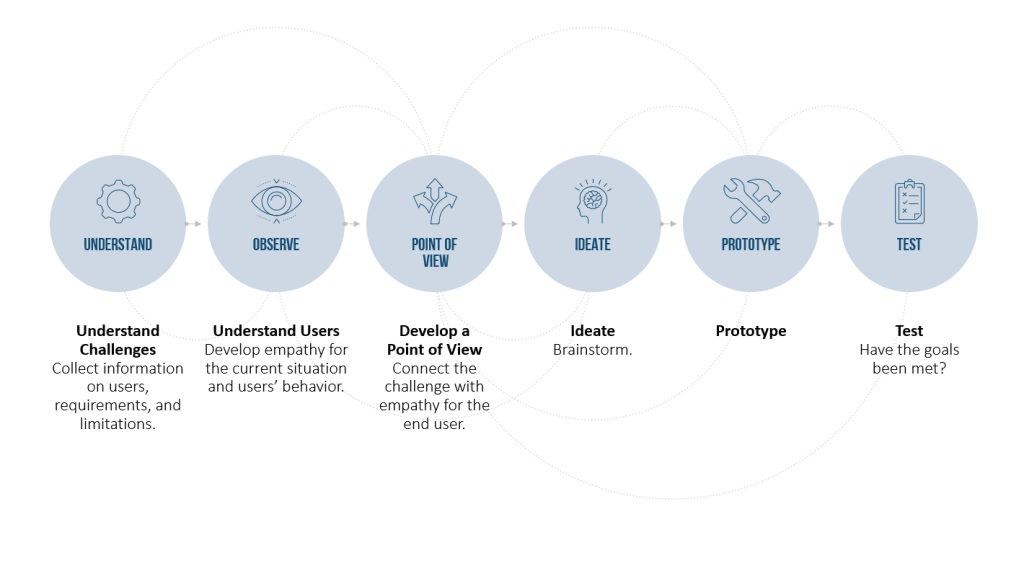
The Design Thinking process model consists of six phases, during which the problem evolves through an idea to a solution. The phases are:
Phase 1: Understanding the problem and empathizing with the customer
The first thing to do is to look at the problem from all sides and understand all possible perspectives. This requires good research work, as the only way to guarantee that the problem has actually been understood.
Collecting all relevant materials and documents is time-consuming, but essential for the next steps. The team members involved should acquire expertise and grasp the core of the problem, which is often not obvious. This process is needed to find the right solution to the problem.
Phase 2: Observation
In the second step, the team interacts with the target group and builds empathy with the customer. This is done by observing and interviewing people relevant to the problem in their respective environments (these people do not necessarily have to belong to the target group).
It is important not to be mentally limited by assumptions and prejudices and so overlook crucial information. Phase 2 should not only be theoretical; the team should leave the office premises and experience the everyday life of the relevant groups on site.
Phase 3: Synthesis
In phase three, all the collected information, data, materials, insights and results are compiled and visualized. It is important that all team members have access to all information and that a real exchange takes place.
Phase 4: Generating ideas
Now the active search for solutions and new ideas begins, with the goal of generating as many solution approaches as possible. The focus on the customer’s interests during the search for solutions increases the efficiency and productivity of the group; at this stage, new ideas are collected but not yet evaluated,.
Finally, all ideas are structured and filtered using four criteria: Attractiveness, feasibility, cost-effectiveness and greatest possible customer benefit.
Phase 5: Developing prototypes
To find concrete solutions and answer specific questions, phase five is when prototypes are developed. At this point, ideas and observations are transferred to the physical world. Ideas can be tried out and evaluated on the basis of these prototypes.
Phase 6: Testing the prototypes
The prototypes previously developed are repeatedly subjected to further testing and feedback loops. Feedback from the target group generates further starting points for improvements, refinements or alternative prototypes.
Design Thinking templates for PowerPoint
To really get the most out of your Design Thinking, we recommend professionally designed slides from PresentationLoad. Our templates will help you to find the solutions you need.

Do feel free to have a look around our store! ►To the store
To sum up: Design Thinking: 6 Steps to a Solution
Design thinking is a method that helps people articulate problems and generate solutions (in the form of products, services etc). It helps to overcome unconscious boundaries and to think outside the box. This is how novel and creative approaches emerge.
Why not try the Design Thinking model the next time you have a problem? It’s sure to get you to the solution you need.
Got any questions about the article? Please feel free to email us at [email protected]. We’re always happy to help!
Looking for visually supportive and professionally designed slide templates? Feel free to take a look around our store. We have a huge range of professionally designed slides for you to download across a wide variety of business topics. Take a look today! ► To the store
You might also be interested in the following articles:




