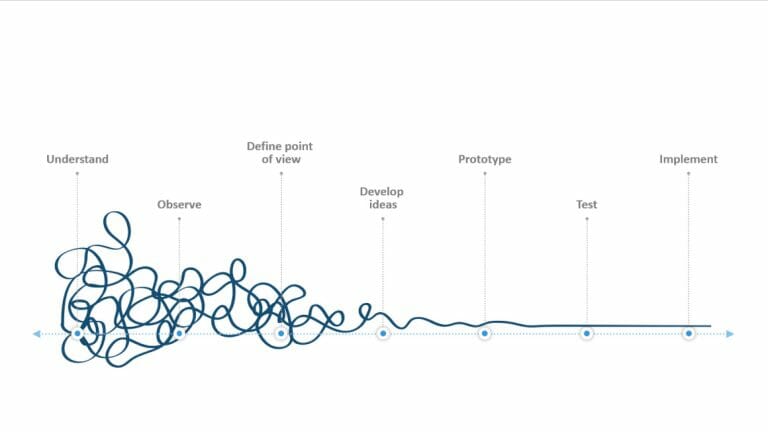
Problem-Solving with 8D and 7STEP
An effective approach to problem-solving is crucial for success in businesses and projects of all kinds. Problems should be solved systematically and thoughtfully. One possible method for this is the 8D process, originally stemming from quality control, and the 7 steps (7STEP) for effective presentations.
Discover how these two approaches merge to not only solve problems but also create compelling presentations that convey your message clearly and effectively.
The significance of 8D and 7 STEP for PowerPoint presentations
Do you receive complaints or feedback regarding your products or services? Take these responses seriously to maintain customer satisfaction and optimize the quality of your offerings.
Both the 8D (8 Disciplines) and the 7STEP processes are similar, structured problem-solving methods that assist you in mastering product or process issues. Both methods are used for addressing customer complaints. With 8D and 7 STEP, you can bring structure, clarity, and effectiveness to the presentation process.
When we apply this structured approach to presentation development, it helps optimize the entire process. In contrast, the 7 steps for effective presentations provide clear guidance for creating compelling and targeted presentations. They help focus on the audience and the message, ensuring a meaningful structure that facilitates the conveyance of information.
In combination, 8D and 7STEP contribute to creating presentations that are not only informative but also engage and persuade the audience. This allows businesses and professionals to present their ideas, products, and projects more effectively and achieve their goals.
In the following, we will explain the processes and demonstrate how to handle your complaint management professionally.
What is 8D?
8D stands for “8 Disciplines” and is originally a quality management tool developed in the automotive industry. It provides a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving and process improvement. The 8D method consists of eight well-defined steps aimed at analyzing problems, identifying their root causes, and developing permanent solutions.
The history of 8D dates back to the 1980s and was initially introduced by Ford. Since then, this method has proven to be highly effective in various industries and is applied worldwide.
Applying 8D to presentation development offers a disciplined approach to ensure that presentations are well-structured, persuasive, and effective. This leads to presentations that are not only based on facts but also capable of engaging and inspiring the audience, which is crucial for the success of any presentation.
The 8 Steps of the 8D Problem-Solving Process
Step 1: Team Formation The first step in the 8D process involves carefully assembling a multidisciplinary team. Team members should bring diverse skills and perspectives to ensure comprehensive problem-solving. This team will accompany the entire journey to solve the problem and is crucial for the process’s success.
Step 2: Problem Definition This step involves defining the problem clearly and precisely. An accurate problem statement allows the team to focus on the essential aspects and ensure that resources are effectively utilized.
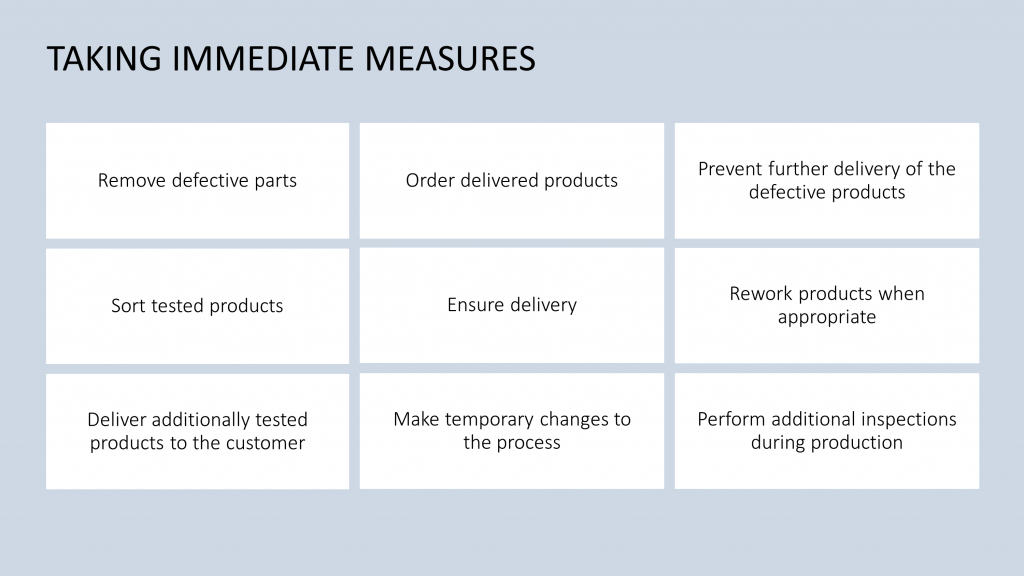
Step 3: Immediate Actions Immediate actions are taken in this step to limit potential damage and restore immediate stability. This may involve implementing temporary solutions to address acute issues and minimize their impact on processes or products.
Step 4: Root Cause Analysis Identifying the roots of the problem is the core of Step 4. Various analysis tools and methods are used to determine the underlying causes of the problem. This step forms the basis for developing sustainable solutions.
Step 5: Solution Generation In this step, potential solutions are developed. The team uses creative approaches and analytical techniques to create a range of possible solutions. It is essential to evaluate different ideas and select those best suited for problem resolution.
Step 6: Solution Implementation Once a solution is chosen, implementation takes place. This step requires careful planning, resource allocation, and monitoring to ensure that the solution is effectively executed.
Step 7: Prevention Prevention is key to avoiding future problems. Measures are developed and implemented to ensure that the problem does not recur. This may involve training, process changes, or quality improvements.
Step 8: Closure and Recognition The final step of the 8D process includes reviewing the entire process, documenting the results, and recognizing the team’s efforts. Thorough post-analysis is crucial to ensure that the insights gained can be applied in the future.
What is 7STEP?
The 7STEP model is a framework for improving presentations and communication skills. It is a useful tool to ensure that presentations are effective and goal-oriented. It also emphasizes the importance of systematic approaches to presentations and their preparation.
It consists of seven steps:
- Objective Setting: Clearly define the goal of your presentation. What do you want to achieve? This step helps determine the focus of your presentation.
- Audience Analysis: Understand your audience. Analyze their needs, expectations, and knowledge level to tailor your presentation to them.
- Structuring Content: Develop a clear outline and structure for your presentation. This helps present information logically and comprehensibly.
- Visualization and Design: Choose appropriate visualizations and design your slides effectively. Visual elements can support and illustrate your message.
- Presentation Techniques: Learn presentation techniques to effectively convey your message. This includes aspects such as voice, body language, and audience interaction.
- Feedback and Adjustment: Gather feedback from others and adjust your presentation accordingly. This enables continuous improvement.
- Preparation and Delivery: Thoroughly prepare for your presentation and deliver it to your audience. In this step, you apply the techniques learned to communicate your message clearly and persuasively.
Juxtaposition of 8D and 7STEP
The 8D and 7STEP methods of problem-solving have proved themselves effective in different industries, especially the automotive industry. The demands of the customer determine which method to use, however the sequences and procedures are both similar, as shown in the picture below:
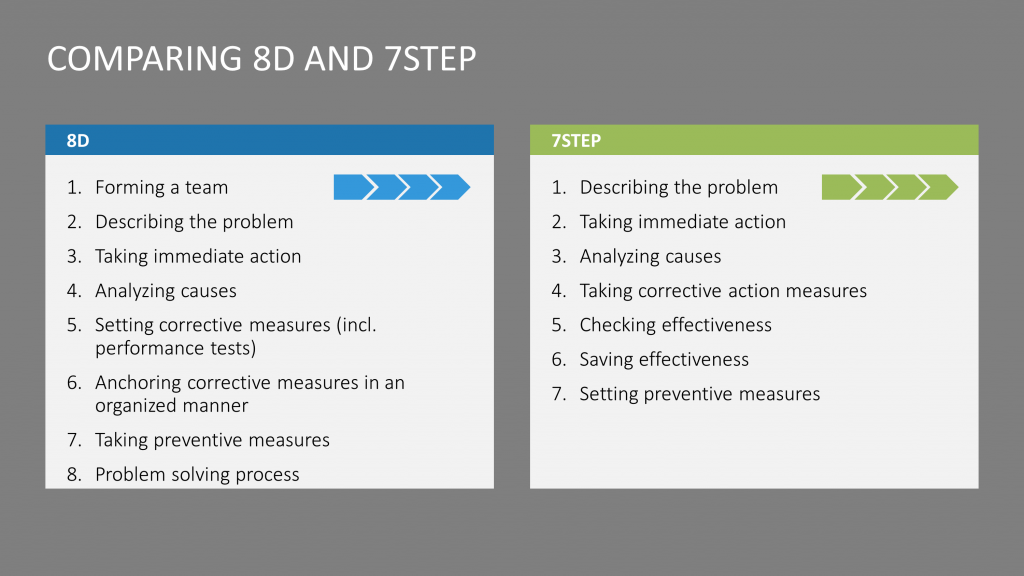
There are two main differences between the two processes. In the illustration, the team formation (step 1 in Figure 8D) and the conclusion of the problem-solving process (step 8 in 8D) are not present in 7STEP. However, in theory, these steps also exsist in 7STEP, as in you start by gathering a team and you end with a final conclusion.
In the 7STEP structure, defining, testing and implementing corrective actions are listed differently than in the 8D model. For example, efficacy testing is included in step 5 of 8D, while in 7STEP, it is its own separate step.
Step by step problem-solving
The integration of 8D, the structured problem-solving approach, and the 7 steps to effective presentation can lead to a powerful combination. Both models share the common idea of a systematic and disciplined approach based on clear steps and goals. Here are some ways they can be interconnected:
- Clear Objective Setting: Begin both problem-solving and presentation preparation with a clear objective. In the 8D process, you define your goal, usually resolving an issue, while in presentations, you establish the goal of your message.
- Audience Analysis: Understanding the audience is crucial in both approaches. In the 8D process, you analyze the causes of a problem, which also requires an understanding of the affected stakeholders. In presentations, you need to grasp the needs and expectations of your audience.
- Structuring: Clear structure is important in both problem-solving and presentation development. In the 8D process, you structure your approach, while in presentations, you organize your content logically and comprehensibly.
- Visualization: Visualization of information plays a role in both models. In the 8D process, you use charts and analyses to illustrate data, while in presentations, visualizations help clarify complex ideas.
- Presentation Techniques: Presentation techniques learned can also be useful in communication within the 8D process. They help in presenting your insights and solutions clearly and persuasively.
- Feedback and Adaptation: An iterative approach is essential in both models. You collect feedback and adapt your approach or presentation to achieve continuous improvements.
In general, the steps can be divided into three phases:
- The first phase aims to assemble an expert team that addresses the problem to the extent that the customer is no longer confronted with it by initiating immediate actions.
2. In the second phase, the problem is intensively analyzed until the root cause is identified. The 5 Whys method is suitable for this, as it simplifies the problem to the error-causing step through various “why” questions (it is permissible to ask more than 5 “why” questions, contrary to the method’s name). Subsequently, corrective actions are identified and tested for long-term effectiveness.
3. In the third and final phase, the found solutions are anchored organizationally (updated work instructions, training, etc.) and technically (changes to machinery, etc.) within the company. In addition, preventive measures are taken to prevent a recurrence of the same error elsewhere. The Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is often used for this purpose, to identify and eliminate weaknesses in plans for future products/processes where the identified problem may occur.
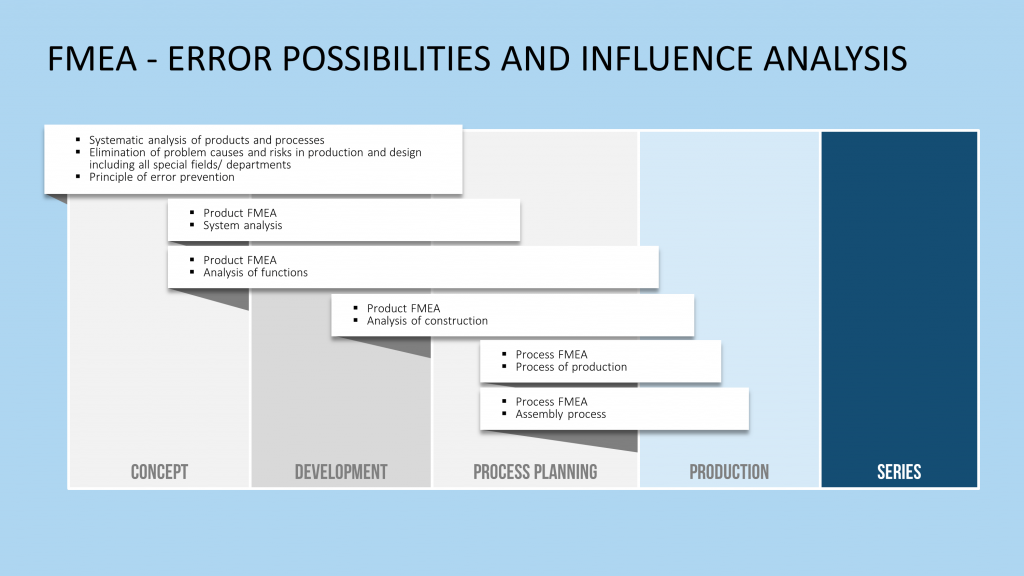
Feel free to use FMEA templates from PresentationLoad!
Customer satisfaction and loyalty
Do you wonder whether the time and energy-consuming problem-solving processes are worth the effort? Of course, considering the severity of the problem, it may be quicker to solve it without the help of 8D/ 7STEP.
Yet, every business that commits to the saying, “the customer is king” should invest in an expert team that analyzes complaints and works out problems to the full satisfaction of it’s customers.
With the help of 8D/ 7STEP, rapid emergency measures are initiated, long-term, solutions are developed and chances of repeated errors are eliminated. All of this ultimately benefits you by gaining customer satisfaction, customer loyalty and higher product quality.
Take advantage of our 8D/ 7STEP templates for PowerPoint with detailed explanations of each step of both methods, templates for root causes of problems, roadmaps, charts, and more for implementing successful complaint management. View PowerPoint templates here.
Conclusion: Skillfully Combining 8D and 7STEP
The integration of 8D, the structured problem-solving approach, and the 7 steps to effective presentation represents a powerful method for optimizing internal processes and enhancing external communication. These models offer clear and disciplined approaches that can be applied in a variety of business contexts.
Emphasizing clear objectives, thorough audience analysis, and thoughtful content structuring helps efficiently address problems and create convincing presentations. This integrative approach provides companies with the opportunity to increase their effectiveness and impact in an increasingly demanding business world.
If you have any questions about the article or PowerPoint presentations in general, feel free to contact us at [email protected]. We are here to assist you!
You can find professionally designed slide templates to enhance the impact of your presentation in our shop. Take a look around; we have numerous slides on various (business) topics. ►Shop Link
You might also be interested in these articles: