The Best Presentation Structure: Tips & Tricks!
The name PowerPoint says it all – a powerful tool for visualizing expressive content. With the right presentation structure, PowerPoint helps add weight to your ideas and statements through visual impact.
Are you looking for the perfect presentation structure that provides lots of opportunities to inspire your audience? Not exactly sure where to start? Keep reading for a detailed guide that will guarantee success.
Prep work
As a rule, a presentation needs a topic and a specific reason for presenting it.
Here are some examples:
- A sales presentation to a customer to introduce products or services
- Presenting company figures to management
- An onboarding presentation to inform new colleagues about the most important company information
- A presentation for your company’s anniversary
- Presentations for school or university
- A presentation of research results for a science conference
Regardless of the topic or occasion, you need a clear and well-thought-out presentation structure. Without that, your audience will have a tough time following and your presentation will fall short of its goal, like attracting a new customer.
Give yourself enough time
Give yourself enough time to prepare your PowerPoint presentation. As soon as you know when you’re presenting, create a schedule. Spend 30 minutes a day preparing your upcoming presentation. Allow enough time to research the material, too. Use the rule of thirds as a guideline: If you have twelve days until the presentation, devote four days to researching and collecting information.
Take the time to thoroughly research your presentation topic. Take notes, collect ideas and thoughts. Use something you always have with you; a small notebook, a tablet or your smartphone is all you need. Keep your notes short – just enough information to get your creative juices flowing.
Organize your notes

Once you have enough material, it’s time to organize and structure it. Now is the time to form your basic presentation framework. Remember to allot enough time for this (think about the 3/3 rule).
Use your notes to develop your presentation. Ask yourself this: What’s the goal of my presentation? For example, do you want to impress investors with your startup or present an innovative marketing plan for the coming fiscal year? Answering this question will help you develop a core thesis.
Here’s something else to ask yourself: What do you want from your audience? Do you want to prompt an action (e.g., buy a product) or kick-start a discussion?
The go-to PowerPoint structure
Now that you’re prepared, it’s time to think about the right PowerPoint presentation structure. Here’s a general guide:
- Introduction
- Topic component 1
- Topic component 2
- Topic component 3
- Conclusion
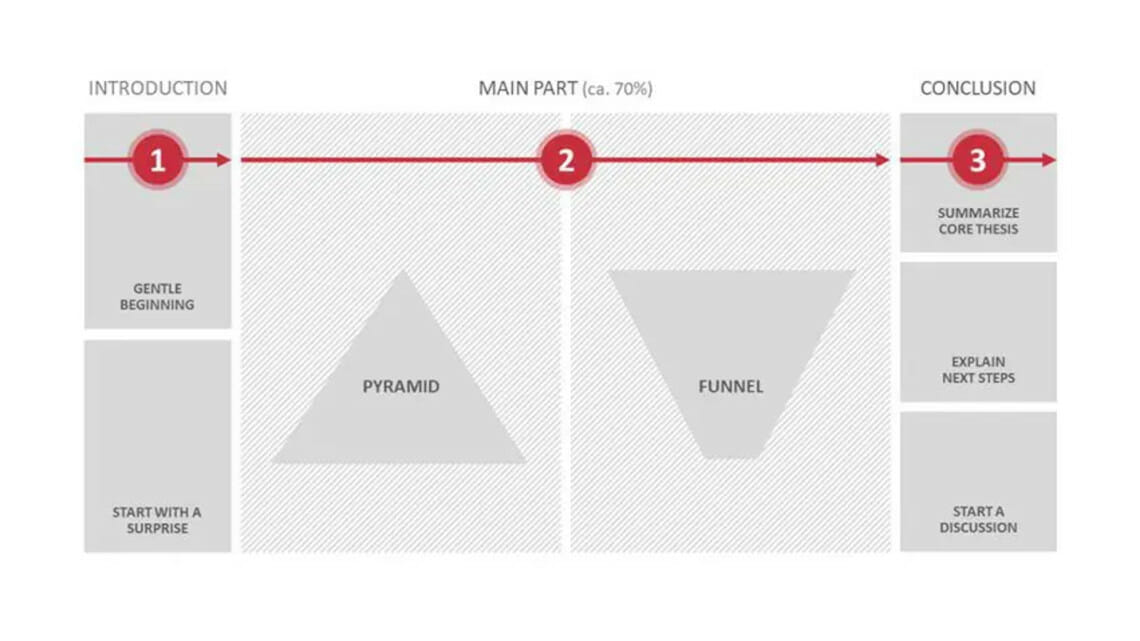
Remember to balance the various parts of your presentation. As a rule, the introduction shouldn’t be more than two slides. The topic slides form the body and should make up about 70% of your PowerPoint presentation. As simple as this may sound, it can be difficult to know which stylistic devices or elements to use to keep your audience’s attention. What should you focus on in each section of the presentation?
Take a look at this chart outlining a presentation:
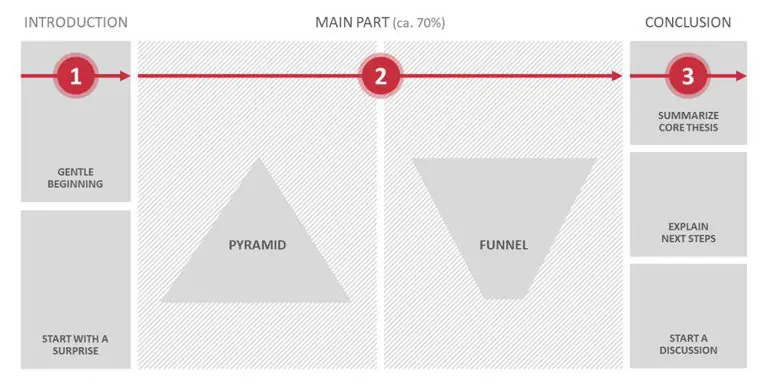
So, what does this mean for each part of the presentation structure?
1. The introduction: Pique curiosity
An intro is an important part of any presentation structure. It has to awaken the audience’s interest and ideally, create a rapport. There are several ways to start the presentation.
- The soft intro
With this type of introduction, you meet the audience at their level and gradually get to the core content of your presentation. Your first slides should be simple and not introduce too much new content. The audience should be able to understand and agree with all points until you finally get to the main topic. The first step is to describe the current situation, the second step to describe the challenge and the third step to discuss how to respond to the challenge.
- The “element of surprise” intro

With this introduction, the element of surprise is on your side. Start the presentation with a statement that shocks or surprises your audience. Bold statements or results from studies are excellent ways to do this. With this kind of intro, you also describe the current situation and what has happened or could happen. You outline the potential consequences and ask how it should be handled. Make sure these statements are true and relevant to your audience. If they aren’t, you’ll come off as less credible.
2. The body of the presentation: The heart of the matter
The body should make up about 70% of your presentation structure. This is where you flesh out your presentation topic. Put yourself in your audience’s shoes; how you would like a presenter to address you? Are their arguments valid? This is a great time to actively involve your audience in a question-and-answer scenario. This is called a dialogue-oriented presentation. Involving your audience this way guarantees their full attention.
There are two ways to organize the main part of the presentation:
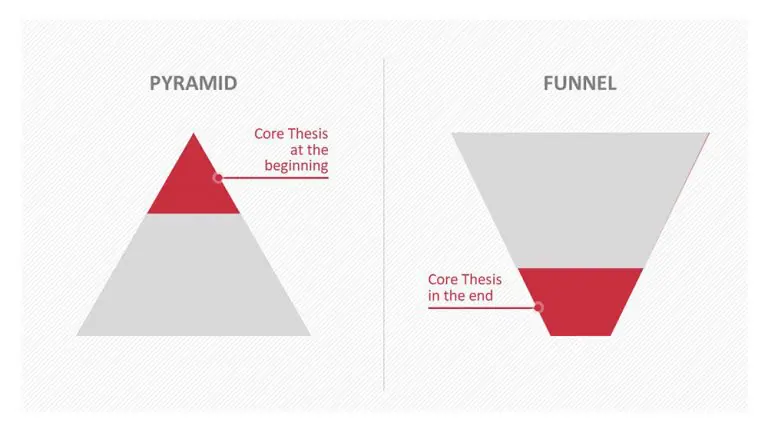
- As a pyramid
With this structure, the core message is introduced at the beginning of the presentation’s main section. Presenting the core message early will have your audience wanting to hear more. This is exactly the right time to start the question-and-answer scenario to hold their attention and get them involved.
- As a funnel
The funnel introduces the core message towards the end of the presentation. This structure does have a few drawbacks. It doesn’t lend itself well to a dialogue-oriented presentation and by waiting until the end to deliver your core message, your audience may not make the connection with earlier key statements. To avoid this, it always helps to revisit those earlier statements and reinforce the core message.
It’s also a more challenging presentation structure to pull off, especially if you don’t have that much experience with presenting. The funnel can be effective with controversial and/or highly emotional topics. Controversial core messages that are brought up at the very beginning of a presentation can lead to discussions that veer off and are hard to control. In these cases, the funnel structure is the better option.
3. The conclusion: crossing the finish line
The final part of your presentation structure may seem like the easiest. You’ve presented all your content, so the hard part is over, right? Never underestimate the importance of your conclusion. It gives you the perfect opportunity to reiterate your key points. Use it to summarize your insights, draw a conclusion and finally, discuss what needs to be done next.
It’s also a great opportunity to initiate an open discussion. If you want to open the floor to comments and questions at the end, give your audience a heads-up at the beginning of your presentation. That will give them a chance to take notes as you go along. You could also encourage the audience to ask questions during the presentation. Do this only if you know you won’t get thrown off track and you can quickly shift gears while presenting. You can find more helpful tips for a successful end of presentation here.
How to apply these tips now and create a presentation from scratch can be found in this tutorial.
The right presentation structure: It’s not just about content
Don’t forget that content alone is not enough to convince your audience. A well thought-out and rehearsed presentation is also counts as part of a presentation’s structure. The right delivery supports your slides and opens the door to communicating with your audience. You can find many helpful tips on giving a presentation in these articles:
- Why a good presentation intro is so important
- Tips for closing out a presentation
- Using the right body language while presenting
- Public speaking skills
- How to handle mistakes and slip-ups while presenting
- Using humor in presentations
Pro tip: Use notes
Is your presentation ready? Now it is time to prepare for your delivery. A short script may help. Just make sure you provide additional information and don’t simply read the slides aloud.
You can choose any note-taking tool you like. You can either use classic index cards with keywords or the Notes function in PowerPoint. You can read more about this here.
Most importantly, practice your presentation. Speaking freely and confidently is key to your presentation’s success. As great a tool as it is, PowerPoint can’t do it all for you; it can only visually support your key messages. So, take the time to make sure you are as well prepared as possible.
Impress your audience: Deliver a strong presentation with the perfect structure!
PowerPoint gives so many advantages to you and your presentation. PowerPoint is so easy to use, even beginners can master it in just a few simple steps.
Follow our tips on the right presentation structure – you’ll be amazed at how easy it is to create a professional and cohesive PowerPoint presentation!
If you need help developing the right presentation structure or building your presentation, let us put our expertise to work and help you create the perfect presentation. Feel free to contact us here for a no-obligation estimate or email us at: [email protected].
Are you looking for professionally designed slide templates for your presentation? Then take a look at our shop. We have templates on a diverse selection of business topics and design themes for you to download. For example, these:
These articles might also interest you: